Everyone knows such examples: HE, a risk-taker, speeds down the highway at 250 km/h, while SHE sits fearfully in the passenger seat, shouting “Careful!” Or in the office: The harmony-seeking colleague is already organizing the next feel-good team event, while the egomaniacal colleague is busy trying to climb to the top of the career ladder.
At least that is the common prejudice regarding psychological differences between men and women.
But have you ever wondered whether the sexes really tick as differently as stereotypes sometimes lead us to believe? Are men from Mars and women from Venus? Or are we more similar than we think?
How do psychological differences between men and women arise?
The question of why men and women sometimes differ in certain behaviors or preferences is a perennial one. Are such things innate (i.e., natural) or the result of social conditioning? Scientists are intensely debating the true influence of biology, upbringing, and culture.
The truth, as is so often the case, probably lies somewhere in the middle.
This means that the causes of gender differences are a mix! Biological predispositions, the way we are raised, and the culture that surrounds us – all of this interacts and shapes our psychological “map.”
Specifically, it is a complex interplay of these factors that are decisive for the psychological differences between men and women:
Biological aspects: What nature gives us
Men’s and women’s bodies are not the same, nor are their brains. This can also affect their psyche. But be careful: This doesn’t mean that one gender is “better” or “worse,” but simply that there can be naturally different average values for certain characteristics .
It’s also important to note that biological differences are tendencies, not fixed patterns. They may create a certain basic disposition, but how this manifests itself in detail depends heavily on other factors.
The brain:
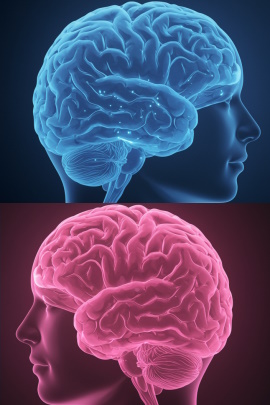
There are subtle differences in the structure and functioning of male and female brains. For example, men have a slightly larger brain volume on average, while women tend to have denser connections between the brain hemispheres.
Some researchers suggest that this could contribute to differences in spatial awareness (often cited as a strength in men) or in the ability to multitask and empathize (often attributed to women) .
But be careful of generalizations!
These psychological differences between men and women are averages, and the individual range is enormous. There are men with outstanding empathy and women who excel in spatial reasoning. Furthermore, our brains are extremely plastic, meaning they change throughout our lives through experience and learning.
Genes and hormones:
Our genes and hormones also play a role. The Y chromosome in men and the varying concentrations of hormones such as testosterone and estrogen not only influence our physical development but can also shape behavioral tendencies.
Testosterone, for example, is associated with dominance behavior and risk-taking, while estrogen and other hormones can influence emotional processes. A classic example is the female menstrual cycle, which can be accompanied by mood swings in many women.
But here, too, hormones are only one piece of the puzzle and don’t explain everything. And yes, men also have estrogen and women have testosterone, just in much smaller amounts!
Evolutionary perspective:
Some psychological differences between men and women are also explained by evolutionary reasons. In prehistoric times, men and women often had different roles (hunters vs. gatherers/childcare workers).
These roles may have favored certain abilities and behaviors over millennia. For example, better spatial orientation in men for hunting or stronger social bonding skills in women for group cohesion and child rearing.
Whether these evolutionary influences are still as important today is controversial, but they offer an explanation.
Education: How we are “made” into men and women
From an early age, boys and girls are often treated differently, consciously or unconsciously. This starts with the color of their rompers (blue for HIM, pink for HER) and extends into many areas of life and upbringing:
Toys and play behavior:

Boys are more likely to receive cars, building blocks, and action figures as gifts, which can encourage spatial thinking, competition, and interest in technical topics. Girls are more likely to receive dolls, play kitchens, and craft sets, which may encourage social interaction and nurturing.
If a boy prefers to play with dolls or a girl enthusiastically builds with Lego Technic, this is sometimes still viewed with skepticism.
Already here, during children’s play, important foundations are laid for the later psychological differences between men and women, right up to the choice of career (see below!).
Expectations and role models:
Boys are often expected to be strong, brave, and not whiny. They then hear sayings like, “An Indian knows no pain!” Girls, on the other hand, are expected to be sweet, well-behaved, sensitive, and helpful.
Such expectations shape children’s self-image and behavior. If boys constantly hear that they shouldn’t be “like a girl,” they may be more likely to suppress their feelings.
Praise and criticism:
Studies show that boys and girls are often praised or reprimanded for different things. Boys are praised more for assertiveness, girls more for cooperativeness. This reinforces certain behavioral patterns.
These educational influences shape us profoundly. They teach us what behaviors are considered “typically male” or “typically female” in our society and how we should behave to be accepted.
Cultural influence: The stamp of society
Closely linked to upbringing is the influence of the social environment in which we grow up. Every culture has its own ideas about masculinity and femininity. This also fosters psychological differences between men and women:
Media and role models:
Films, series, advertising, magazines and social media often convey stereotypical role models: the strong action hero, the caring mother, the cool alpha male and daredevil, the seductive beauty.
These images shape our perceptions and our expectations of ourselves and others. Even though things are slowly changing and more diverse role models are being presented, old patterns often still have a strong impact.
Career choice:

In many cultures there are still “typical male professions” (e.g. engineer, craftsman) and “typical female professions” (e.g. educator, nurse).
This is of course due to different interests, but also to social expectations and structures that make access to certain professions easier or more difficult.
Working in a traditionally male-dominated profession is one reason why some men remain single forever . Unlike other men, they have difficulty finding the right partner at their workplace because the selection of women there is far too limited.
Social norms:
How openly are men allowed to express their feelings? How much space are women allowed to occupy in (public) discussions, such as corporate meetings or talk shows? Such norms vary greatly across cultures and history and influence gender behavior.
This reinforces psychological differences between men and women.
Cultural conditioning is like a pair of glasses through which we see the world and which tells us what is considered “normal” for men and women.
Or when was the last time a woman approached you at a party? Has it been a long time? No wonder! In our society, it’s considered normal for us guys to be the “hunters” and have to approach women , because women tend to take a more passive role when it comes to flirting and dating.
The most effective plan: From “Hi” to a date
I’ll also tell you a 97% rejection-proof method: how to overcome your fears, approach the woman of your dreams in a relaxed manner, and seduce her into a kiss on your date.
The best part is: This simple guide works for EVERY man, no matter what you look like, how confident you are, or how much money you earn at work.
So if you want to make women fall in love starting today…
…then click the “Play” button now and watch my short video to learn how to maximize your success in approaching, flirting, and dating IMMEDIATELY!
Typical man, typical woman? 12 psychological differences in everyday life under the microscope
Let us now turn to some specific areas in which psychological differences between men and women are often discussed.
But always remember: We’re talking about averages and trends here. The differences within gender groups are usually much greater than the differences between them!
Character traits and behavior in everyday life
The sexes are often attributed opposing characteristics, fueled by clichés in films. For example, we see the brawling hero who bravely faces all dangers – and the caring beauty who tends to his (physical and emotional) wounds after a successful fight.
But is this true, or are these just cheap clichés? Indeed, such prejudices have a kernel of truth:
1. Aggression:
On average, men across cultures exhibit more confrontational, physical aggression than women (such as a bar fight). This is often attributed to the influence of testosterone and evolutionary factors.
Women, on the other hand, may be more prone to indirect, relationship-oriented aggression “behind the back” of the person affected (e.g. gossiping, social exclusion, plotting, ignoring ).
Of course, this doesn’t mean that all men are physically aggressive and all women are sneaky snakes! The issue is much more complex, and aggression can take many forms in both sexes.
2. Risk-taking:

Psychological differences between men and women also exist in areas where risks and dangers are concerned.
On average, men tend to take more risks, whether in traffic, financial decisions, or extreme sports. Hormonal and evolutionary factors may also play a role here.
Female representatives, on the other hand, are often described as more security-oriented, cautious, and less risk-averse. This is also considered one of the reasons why so few women are active in poker .
But as you can probably imagine, there are also countless risk-taking women and very cautious men.
3. Empathy and caring:
Women often score higher in studies of empathy and caring. This could have biological causes (e.g., hormonal influences, evolutionary maternal roles), but could also be socially influenced by nurturing behavior.
However, empathy can be learned and many men are very sensitive and caring, even if they may show it differently.
4. Competitive orientation:
Men are often described as “competitors,” while women are more cooperative and in need of harmony. This is sometimes even evident in children’s play behavior.
Whether someone is more competitive or cooperative depends heavily on the situation and individual goals. Women can be just as ambitious and competitive, for example, in sports, politics, or their careers. However, they may choose different strategies.
5. Willingness to help:

Studies on helpfulness show a mixed picture regarding the psychological differences between men and women:
Men are often more likely to help in situations that require courage or physical strength. For example, there’s the heroic and protective type who steps in when a woman is sexually harassed on her way home in the dark. Or the buddy type in the friend zone who helps carry his best friend’s furniture when she moves .
Women, on the other hand, are more likely to help in situations that require care and emotional support, such as comforting someone who is heartbroken.
But the willingness to help is a deeply human trait that is not strictly gender-specific.
6. Interests:
There tend to be gender differences in hobbies and interests. On average, men are often more interested in technical things, while women are more interested in social or artistic areas.
However, these interests are strongly shaped by upbringing, social opportunities, and expectations. And who says a woman can’t be passionate about technology or a man can’t be socially engaged?
It is also common knowledge that there are numerous male artists, from painters to writers to heavy metal guitarists.
Emotions: emotional vs. rational?
Another area that is surrounded by many clichés is the emotional world. There are supposedly major psychological differences between men and women here. While men are said to be more logical, intellectual, and cold-hearted, women are often associated with strong emotions and a lot of passion.
Let’s take a look at what is fact and what is more of a myth:
7. Emotional expression:

Women are often said to be more emotional. However, upon closer inspection, it’s often more about the expression of emotions. Women tend to speak more openly about their feelings and also express them more clearly through facial expressions and gestures.
Men have often learned to suppress certain “feminine” emotions (especially sadness or fear) and adopt a mask of strength and coolness like James Bond. At the same time, anger and rage are considered more “masculine,” which is why they are more “allowed” to express such emotions.
But that doesn’t mean that men feel less overall! They may just channel their emotions differently.
8. Stress management:
Men are more likely to engage in “fight-or-flight” responses to stress, while women are more likely to show nurturing, seek social support, and strengthen their bonds with family and friends. Such patterns of female stress response are referred to as “tend-and-befriend.”
This psychological difference between men and women could be related to different hormonal responses to stress. However, there are many individual coping strategies here, regardless of gender.
9. Mood swings:
Are women moody and fickle? More so than us guys? In a way, yes! Hormonal cycles can indeed cause mood swings in women. But men also experience mood swings, although they are influenced by other factors (stress, success, etc.).
The cliché of the “stoic, equanimous man” and the “hormone-driven woman” who is feared for her unpredictable emotional outbursts is therefore often exaggerated.
Do you finally want to conquer your dream woman?
For a long time, I only shared this #1 trick with my coaching clients. With it, I’m able to easily seduce women in conversation, so they suggest a date on their own!
The best part is: This trick works for EVERY man. You don’t need excessive self-confidence, a toned body, or a bank balance as high as Bill Gates.
So if you want to learn today how to get a whole lot closer to your dream woman…
…then click the “Play” button now and watch my short video to learn how to maximize your flirting success when approaching and dating IMMEDIATELY!
Communication: direct vs. indirect style?
To say it right away: There are communication differences between the sexes, but they are often more subtle than one might think.
Misunderstandings often arise not because men and women speak “different languages,” but because they sometimes have different goals and expectations for a conversation. Listening and asking questions always helps!
Who communicates how always depends on the specific situation, the person being communicated with and other factors.
Let’s take a closer look at the communication differences between men and women:
10. Discussion objectives and content:

Are these psychological differences between men and women to blame for the fact that they so often talk past each other in everyday life?
Men are more likely to use conversations to exchange information, solve problems, or assert their status (reporting style). Women are more likely to use communication to build and maintain relationships, establish emotional closeness, and reach consensus (relationship-oriented style).
But these are just tendencies! A man may simply want to chat, while a woman may present hard facts, for example, in presentations and meetings at work.
Nevertheless, I repeatedly experience single men boring their date partners because they only exchange dry small talk or show off status symbols instead of being humorous and flirting properly .
If you want to change that, you should ask really interesting getting-to-know-you questions on your date and bring up deep-talk topics . This will evoke positive emotions!
11. Conversation style:
The psychological differences between men and women also affect the way they communicate.
Men reportedly interrupt more often, express uncomfortable things more clearly, and speak more in public groups. Women ask more questions, use more affirmative signals (like “hmhm”), and more often use indirect language or “softeners” (like “actually,” “maybe,” “could be,” etc.).
However, how one communicates depends heavily on the situational context, the person being spoken to, and the cultural background. The cliché of the taciturn man and the constant chatterer is just that: a cliché.
12. Nonverbal communication:
Another point is body language: On average, women are often better at interpreting and using nonverbal cues (facial expressions, gestures). But this is also a skill that can be trained and varies greatly from individual to individual.
When flirting, I advise you to always read the woman’s flirting signals to see whether she likes you or is even already in love with you .
At the same time, you should always maintain masculine body language (upright posture, eye contact, smiling, etc.). This will give you a more attractive appearance and make you more appealing to women.
Conclusion: The most important psychological differences between men and women

Yes, there are psychological differences between men and women, based on averages. These differences are rooted in a complex mix of biology, upbringing, and culture.
In summary, these are the most important aspects in which the sexes differ:
Men are on average…
- …physically more aggressive (even under stress)
- …more willing to take risks
- …less empathetic
- …more competitive and “combative”
- …more helpful in situations where courage and physical strength are needed
- …more interested in technology
- …more educated to hide “typically female” emotions in order not to show “weakness”
- …more emotionally stable when it comes to mood swings
- …more direct and fact-oriented in their communication
- …more limited in interpreting and using body language (gestures, facial expressions)
On average, women are…
- …rather indirectly aggressive “behind the back” (instead of confrontational, physical aggression)
- …more safety-oriented, more cautious and less risk-averse
- …more empathetic and caring
- …more cooperative and in need of harmony, less competitive
- …more helpful in situations that require care and emotional support
- …more interested in artistic and social issues
- …more open in their expression of feelings
- …more interested in social relationships (even in stressful situations)
- …more affected by mood swings
- …more emotional, indirect and relationship-oriented in their communication
- …better at interpreting nonverbal signals and using body language
Instead of clichés: examine each person individually!
But, and this is the most important message:
The psychological differences between men and women mentioned above are usually small – and the overlap between the sexes is huge!
Every person is unique, with a unique personality. Therefore, you shouldn’t cling too tightly to stereotypes and labels, but rather look at each person individually to find out what makes them tick.
This is also important when flirting and dating if you are a single man looking for a partner who really suits you!
These tips aren’t all…
Do you want to get the exact step-by-step guide – from overcoming your shyness to flirting to kissing on a date?
Then click on the video now and I’ll tell you 3 more secrets:
- “Anti-rejection technique”: how to overcome fears and approach EVERY woman!
- What you need to say (or write) to make her fall in love!
- The secret #1 kissing trick to win her over on your date!